Name of the ingredient
Nicotinamide riboside chloride (AAN)
Synonyms
Nicotinamide riboside chloride
Definition of the ingredient
Nicotinamide riboside chloride is a single chemical moiety containing nicotinamide and ribose. It is a white to light brown powder that is produced by chemical synthesis and is isolated by centrifiugation.
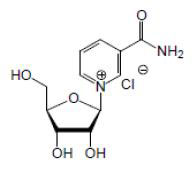
Molecular formula: C11H15N2O5Cl
CAS Number: 23111-00-4
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Description | ||
| Appearance | Visual | White to light brown powder |
| Characteristics | ||
| Solubility in Water | BP General Notices | ≥446.5 mg/mL |
| Melting Point | BP (Appendix V A) | 115 - 125°C |
| Water Content | Karl Fischer USP <921> | ≤1% w/w |
| Identification | ||
| NMR | NMR[1], [2], [3], [4] | Recorded NMR spectra must be in full agreement with the structure of nicotinamide riboside. The percentage of the α and β forms must be determined by comparing the integration of the peak for the anomeric proton for α-nicotinamide riboside (located at ~6.6 ppm with a J coupling value of 5.4 Hz in 1H NMR) and the peak for the β-nicotinamide riboside (located at ~6.3 ppm with a J coupling value of 4.4 Hz in 1H NMR). |
| Assay | ||
| Nicotinamide riboside chloride | HPLC-UV | ≥90% w/w |
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Residual solvents | ||
| Acetone | USP<467> | ≤3000 ppm |
| Methanol | USP<467> | ≤1000 ppm |
| Acetonitrile | USP<467> | ≤50 ppm |
| Methyl tert-butyl ether | USP<467> | ≤500 ppm |
| Incidental metals and non-metals | ||
| Arsenic | USP<2232> | ≤1.0 ppm |
| Mercury | USP<2232> | ≤1.0 ppm |
| Cadmium | USP<2232> | ≤1.0 ppm |
| Lead | USP<2232> | ≤0.5 ppm |
| * The cadmium content in the specification is given as 1 ppm as an upper limit for the ingredient. In the finished product, the cadmium content must comply with the acceptance criteria set out in the United States Pharmacopoeia - National Formulary (USP-NF) general chapter '<2232> Elemental Contaminants in Dietary Supplements' | ||
| Other organic or inorganic impurities or toxins | ||
| Methyl acetate | USP<467> | ≤1000 ppm |
| Acetamide | GC-FID | ≤27 ppm |
| Acetic acid | GC-FID | ≤5000 ppm |
| Microbiology | ||
| Microbiology | USP<61>, USP<62> | Complies with USP<1111> |
Footnotes
| [1] | Syntheses of Nicotinamide Riboside and Derivatives: Effective Agents for Increasing Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Concentrations in Mammalian Cells; Yang, Tianle et al; Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 50 (26), 6458-6461; 2007. |
|---|---|
| [2] | Stereoselective synthesis of nicotinamide β-riboside and nucleoside analogs; Franchetti, Palmarisa et al; Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 14 (18), 4655-4658; 2004 |
| [3] | Syntheses and chemical properties of β-nicotinamide riboside and its analogues and derivatives; Makarov, Mikhail et al; Beilstein J. Org. Chem, 15, 401–430; 2019. |
| [4] | 4. Proton magnetic resonance study of the intramolecular association and conformation of the α- and β-pyridine mononucleotides and nucleosides; Oppenheimer, Norman et al; Biochemistry, 15 (18), 3981-3989; 1976. |
Key to abbreviations
BP = British Pharmacopeia
FID = Flame Ionisation Detection
GC = Gas Chromatography
HPLC = High Performance Liquid Chromatography
ISO = International Organisation for Standardisation
NMR = Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
USP = United States Pharmacopoeia
UV = Ultra-Violet
Product types

